It is formed by the union of the common hepatic duct and the cystic duct from the gallbladder.
Common bile duct dilatation meaning.
It is later joined by the pancreatic duct to form the ampulla of vater.
The bile ducts carry bile from the liver and gallbladder through the pancreas to the duodenum which is a part of the small intestine.
Biliary dilatation when identified may be separated into obstructive or nonobstructive causes.
A biliary obstruction is a blockage of the bile ducts.
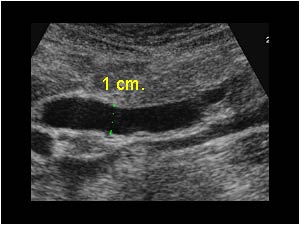
The size of the common bile duct if dilated may suggest a blockage downstream.
Choledochal cyst is a dilatation of the bile ducts outside the liver that is present at birth.
The clinical significance of common bile duct dilatation in patients without biliary symptoms or causative lesions on ultrasonography we detected a significant number of causative biliary tract lesions in asymptomatic adults with dilatation of the cbd on routine abdominal us.
Most commonly the obstruction is caused by a gallstone but cysts or tumors are also possible.
This is a specific finding that is looked for when a patient gets an ultrasound for a suspected liver or gallbladder disease.
The common bile duct sometimes abbreviated cbd is a duct in the gastrointestinal tract of organisms that have a gallbladder.
Primary sclerosing cholangitis results in strictures in the bile ducts and is associated with ulcerative colitis and crohn s disease.
Color doppler can be useful to ensure that dilated structures in the liver are actually bile ducts and not an intrahepatic vascular malformation.
When the bile cannot pass through a particular duct it builds up and the structure becomes distended.
Recurrent pyogenic cholangitis is common in asian countries and is associated with biliary parasites.
Bile duct abnormalities may be identified during evaluation of patient symptoms or laboratory abnormalities or incidentally during imaging for another problem.
Focal dilatation may be a result of downstream stricture or damage to the elasticity of that segment of bile duct possibly from prior stone passage.
1 that due to an obstructive factor localized at the junction of the choledochus with the duodenum as an abnormal angularity or congenital stenosis of the terminal common bile duct and 2 that due to a weakness originating in the common bile duct proper.
A dilated bile duct or one that is enlarged typically occurs when there is an obstruction blocking the flow of bile.